-
Home
-
About JCTR
-
Gold Open Access
-
Issues
-
Editorial board
-
Author guidelines
-
Publication fees
-
Online first
-
Special issues
-
News
-
Publication ethics
-
Partners
-
Submit your manuscript
-
Submit your review report
-
Editorial Office
-

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. ISSN print: 2382-6533 ISSN online: 2424-810X
Volume 9 Issue 3
Acute ischemic colitis associated with oral decongestant use: a systematic review
Muhammad Hassan Naeem Goraya, Faisal Inayat*, Sobaan Taj, Junaid Rasul Awan, Adil Mohyudin, Syed Hasan Ali, Arslan Afzal, Muhammad Junaid Ashraf, Muhammad Adnan Zaman, Zahra Akhtar, Gul Nawaz, Zahid Ijaz Tarar
Goraya et al. J Clin Transl Res 2023; 9(3):8
Published online: May 15, 2023
Abstract
Background and aim: Acute ischemic colitis (IC) has been linked with the use of oral decongestants. However, clinical evidence on this association remains limited. We aim to evaluate the occurrence and clinical outcomes of acute IC following over-the-counter (OTC) use of pseudoephedrine and phenylephrine.
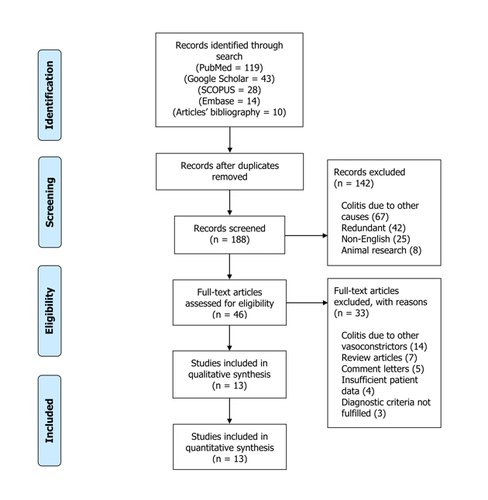
Methods: We conducted a systematic review of the MEDLINE, Google Scholar, Scopus, and Embase databases between inception and July 20, 2022. Specific search terms were used. The inclusion criteria consisted of English-language articles describing acute IC secondary to pseudoephedrine or phenylephrine.
Results: A total of 18 case reports (level of clinical evidence: IV) fulfilled our inclusion criteria. The mean age of patients was 51.6 ± 15.3 years, with 14 (77.8%) cases reported in women. Clinical presentation was mainly related to abdominal pain 16 (88.9%), hematochezia 15 (83.3%), and/or abdominal tenderness 10 (55.6%). The medical background showed that 5 (27.8%) patients were previously healthy. In the 13 (72.2%) patients with comorbidities, hypertension 6 (46.2%), a history of tobacco use 5 (38.5%), and psychiatric illnesses 4 (30.8%) were commonly reported. Leukocytosis was encountered in 13 (72.2%) patients. Diagnostic investigations included a combination of CT scan and colonoscopy in 10 (55.6%), colonoscopy alone in 6 (33.3%), and flexible sigmoidoscopy in 1 (5.6%) patient. Colonoscopic biopsy was the mainstay of diagnosis in 15 (83.3%) patients. Treatment was based on supportive care in 18 (100%), concurrent antibiotic use in 2 (11.1%), and surgical intervention in 1 (5.6%) patient. Recurrent episodes of IC occurred in 4 (22.2%) patients.
Conclusions: Acute IC secondary to oral decongestants remains a rare but important clinical phenomenon. Clinical suspicion and imaging findings are important for early diagnosis.
Relevance to patients: In unexplained cases of IC, clinicians should specifically inquire about oral decongestants since they are OTC and patients commonly fail to reveal their usage. These drugs should be avoided for transient cold symptoms, especially in women.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18053/jctres.09.202303.008
Author affiliation
1. Allama Iqbal Medical College, Lahore, Pakistan
2. Jersey Shore University Medical Center, Neptune, NJ, United States of America
3. University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, MS, United States of America
4. Dow University of Health Sciences, Karachi, Pakistan
5. Woodhull Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY, United States of America
6. University of Missouri School of Medicine, Columbia, MO, United States of America
*Corresponding author
Faisal Inayat
Allama Iqbal Medical College, Allama Shabbir Ahmad Usmani Road, Faisal Town, Lahore 54550, Pakistan.
Tel: +92 321 774 3758
Fax: +92 42 9923 1443
Email: faisalinayat@hotmail.com
Handling editor:
Michal Heger
Department of Pharmaceutics, Utrecht University, the Netherlands
Department of Chemistry, Utrecht University, Utrecht, the Netherlands
Department of Pathology, Erasmus Medical Center, the Netherlands
Department of Pharmaceutics, Jiaxing University Medical College, Zhejiang, China

