-
Home
-
About JCTR
-
Gold Open Access
-
Issues
-
Editorial board
-
Author guidelines
-
Publication fees
-
Online first
-
Special issues
-
News
-
Publication ethics
-
Partners
-
Submit your manuscript
-
Submit your review report
-
Editorial Office
-

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. ISSN print: 2382-6533 ISSN online: 2424-810X
Volume 8 Issue 6
Local anti-inflammatory effect and immunomodulatory activity of chitosan-based dressing in skin wound healing: a systematic review
Karla C. Maita, Francisco R. Avila, Ricardo A. Torres-Guzman, John P. Garcia, Abdullah S. Eldaly, Luiza Palmieri, Omar S. Emam, Olivia Ho, Antonio J. Forte*
Maita et al. J Clin Transl Res 2022; 8(6):7
Published online: November 9, 2022
Abstract
Background and aim: Wound healing is a complex process comprised of several distinct phases. An imbalance in any of the stages creates a chronic wound with the potential to cause life-threatening complications for patients. Chitosan is a biopolymer that has shown to positively impact the different healing phases. This systematic review aimed to evaluate the anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties of chitosan-based wound therapy for the skin healing process after an injury.
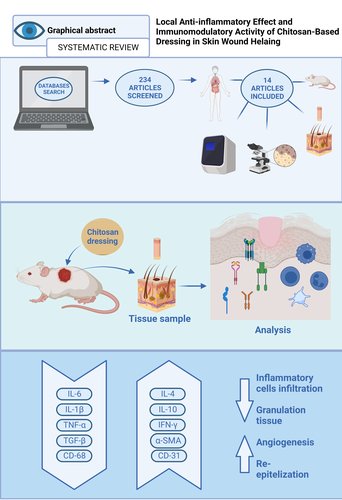
Methods: A systematic review was conducted in November 2021 following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines. The PubMed, Embase, Google Scholar, and Cochrane online databases were queried to capture all publications in the last ten years that investigated the chitosan effects on inflammation and immune reaction.
Results: A total of 234 studies were screened after removing duplicates, and fourteen articles fulfilled our inclusion and exclusion criteria. In the studies, chitosan was combined with a wide range of products. One clinical trial was found that treated patients with diabetic foot ulcers. All animal models in the studies used a full-thickness skin wound to test the effectiveness of chitosan in the healing process. Decreased pro-inflammatory cytokine levels, a shortened inflammatory phase and accelerated wound closure was observed in all of the studies.
Conclusions: Chitosan proved to be a feasible, versatile, and multifaceted biomaterial that enhances the biological response to a skin injury. When combined with other products, its potential to boost the healing process through regulation of the inflammatory and cellular activity is increased.
Relevance for patients: Although few clinical trials have been completed, Chitosan has become an excellent alternative to modulate the local inflammatory response promoting wound healing. Especially in patients with associated comorbidities that affect the typical resolution of skin healing, such as diabetes and vascular insufficiency. Therefore, using bioactive wound dressings based on Chitosan combined with nanoparticles, growth factors, lived cells, or medications, released in a controlled manner positively impacts patient life by shorting the wound healing process.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18053/jctres.08.202206.007
Author affiliation
Division of Plastic Surgery, Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, Florida, USA
*Corresponding author
Antonio J. Forte
Division of Plastic Surgery, Mayo Clinic, 4500 San Pablo Rd, Jacksonville, FL 32224, USA
Tel: +1 904-953-2073
Fax: +1 904-953-7368
Email: ajvforte@yahoo.com.br
Handling editor:
Michal Heger
Department of Pharmaceutics, Utrecht University, the Netherlands
Department of Pharmaceutics, Jiaxing University Medical College, Zhejiang, China

