-
Home
-
About JCTR
-
Gold Open Access
-
Issues
-
Editorial board
-
Author guidelines
-
Publication fees
-
Online first
-
Special issues
-
News
-
Publication ethics
-
Partners
-
Submit your manuscript
-
Submit your review report
-
Editorial Office
-

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. ISSN print: 2382-6533 ISSN online: 2424-810X
Volume 7 Issue 5
Association of dietary total antioxidant capacity with depression, anxiety, and sleep disorders: a systematic review of observational studies
Gabriela Amorim Pereira*, Alessandra da Silva, Helen Hermana M. Hermsdorff, Ana Paula Boroni Moreira, Aline Silva de Aguiar
Pereira et al. J Clin Transl Res 2021; 7(5):5
Published online: September 27, 2021
Abstract
Background and aim: We aimed to systematically review observational studies that evaluated the potential association of the dietary total antioxidant capacity (dTAC) with common mental disorders (depression and anxiety) and sleep disorders.
Methods: Studies with an observational design that evaluated the association between the dTAC and common mental disorders and sleep disorders were identified using the PubMed and Scopus databases. The Meta-analysis Guideline of Observational Studies in Epidemiology and the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis were used to conduct and report the data of this systematic review.
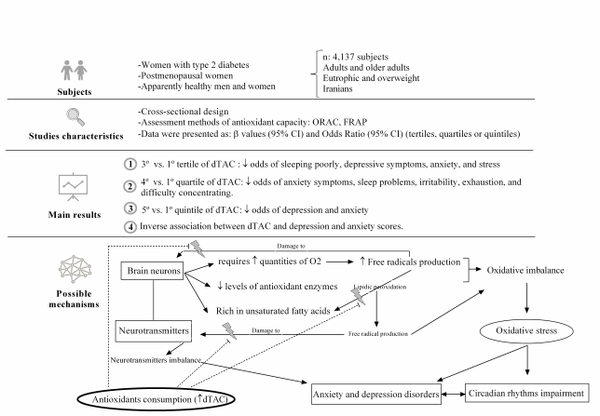
Results: Of the 439 records, seven studies were included in this review. There was a sample variation of 41–3,297 participants. We highlight that five of the studies analyzed were conducted in the Iranian population. Four studies analyzed only women, and three studies were conducted with postmenopausal or climacteric women. Four cross-sectional studies showed inverse associations between the dTAC and depression, anxiety, and sleep disorders in Iranians.
Conclusions: The consumption of a diet rich in antioxidants, characterized by high dTAC scores, seems to be inversely associated with depression, anxiety, and sleep disorders. However, further studies with different populations and designs are necessary for a better understand this relationship.
Relevance to patients: This review assesses the association of the dTAC with common mental disorders (depression and anxiety) and sleep disorders. These knowledge will help guide further studies on the relationship between diet and mental disorders and sleep disorders. Knowledge about these relationships is essential for the creation of non-pharmacological practices for the prevention of these disorders.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18053/jctres.07.202105.005
Author affiliation
1. Faculty of Medicine. Department of Collective Health. Universidade Federal de Juiz de Fora, Juiz de Fora, Minas Gerais, Brazil
2. Laboratory of Energy Metabolism and Body Composition. Department of Nutrition and Health. Universidade Federal de Viçosa, Viçosa, Minas Gerais, Brazil
3. Department of Nutrition. Universidade Federal de Juiz de Fora, Juiz de Fora, Minas Gerais, Brazil
*Corresponding Author
Gabriela Amorim Pereira
Faculty of Medicine. Department of Collective Health. São Pedro Avenue, s/n, university Campus - Zip Code: 36036-900 Universidade Federal de Juiz de Fora, Juiz de Fora, Minas Gerais, Brazil.
E-mail: gabiamorimpereira3@gmail.com
Handling editor:
Michal Heger
Department of Pharmaceutics, Utrecht University, the Netherlands
Department of Pharmaceutics, Jiaxing University Medical College, Zhejiang, China

