-
Home
-
About JCTR
-
Gold Open Access
-
Issues
-
Editorial board
-
Author guidelines
-
Publication fees
-
Online first
-
Special issues
-
News
-
Publication ethics
-
Partners
-
Submit your manuscript
-
Submit your review report
-
Editorial Office
-

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. ISSN print: 2382-6533 ISSN online: 2424-810X
Volume 9 Issue 1
Endurance training and MitoQ supplementation improve spatial memory, VEGF expression, and neurogenic factors in hippocampal tissue of rats
Hanzaleh Jafari Zadeh, Zahrasadat Roholamini, Soheil Aminizadeh*, Maedeh Amiri Deh-Ahmadi
Zadeh et al. J Clin Transl Res 2023:9(1):1
Published online: December 13, 2022
Abstract
Background and aim: The hippocampus has a vital role in memory and learning, which means that this brain structure has high energy demand. Accordingly, mitochondrial dysfunction in the hippocampus has deleterious effects on brain function. MitoQ is an antioxidant that accumulates selectively in mitochondria at high concentration. In this study, the effect of MitoQ alone and in combination with endurance training (ET) was investigated on spatial memory (distance, time, and number of passes in the target quarter), antioxidant status (superoxide dismutase, SOD; glutathione peroxidase, GPx), and neurogenic factor levels (vascular endothelial growth factor, VEGF; brain-derived neurotrophic factor, BDNF) in male Wistar rats.
Methods: Rats were assigned to a control (CTL) group, endurance training (ET) group, endurance training + MitoQ (ET + MitoQ) group, and a MitoQ group. Rats were trained on a treadmill for eight weeks, five days/week, and 50 min/day. MitoQ (250 µM daily) was administered via drinking water for eight weeks. Spatial memory (Morris water maze test), gene expression (Real-time PCR), protein expression (Western blotting), and antioxidants (ELISA method) were determined.
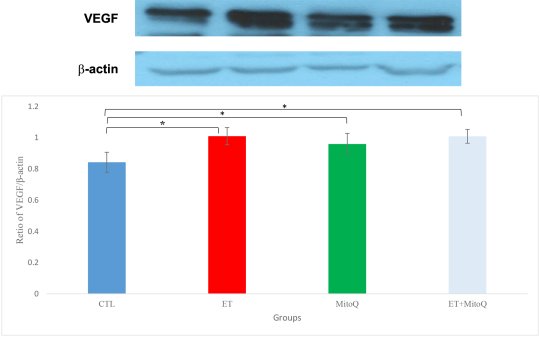
Results: Distance and number of passes in the target quarter in the ET, MitoQ, and ET + MitoQ groups were higher than in the CTL group (P = 0.001). MitoQ + ET had more impact on the abovementioned indices than MitoQ or ET alone. Simultaneous use of MitoQ and ET significantly increased gene and protein expression of VEGF (P = 0.0001) and gene expression of BDNF (P = 0.004) and Sestrin 2 (P = 0.0001) in hippocampal tissue. The expression of VEGF (P = 0.007) and Sestrin 2 (P = 0.001) was higher in the MitoQ group compared to the CTL group. Tissue GPx levels were increased following all three interventions (P ≤ 0.013) compared to the control group while SOD levels remained unchanged in all groups.
Conclusion: The combination of ET and MitoQ has additive effects on spatial memory in rats by modulating parameters that are involved in hippocampal neurogenesis. In addition, MitoQ may have positive effects on the antioxidant defense by improving GPx activity.
Relevance for patients: Considering the positive effects of MitoQ on improving the memory and the antioxidant defense, it seems that it can play a positive role in improving the diseases associated with memory loss in the long term, and endurance training along with this supplement can increase the possible positive effects.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18053/jctres.09.202301.001
Author affiliation
1. Department of Motor Behavior, Faculty of Physical Education and Sport Sciences, Islamic Azad University of Isfahan-Khorasgan branch, Isfahan, Iran
2. Department of Exercise Physiology, Faculty of Physical Education and Sport Sciences, Shahid Bahonar University of Kerman, Kerman, Iran
3. Department of Physiology and Pharmacology, Afzalipour school of Medicine, and Physiology Research Center, Institute of Neuropharmacology, Kerman University of Medical Sciences, Kerman, Iran
4. Cardiovascular Research Center, Institute of Basic and Clinical physiology Sciences, Kerman University of Medical Sciences, Kerman, Iran
*Corresponding author
Soheil Aminizadeh
Department of Physiology and Pharmacology, Afzalipour school of Medicine, and Physiology Research Center, Institute of Neuropharmacology, Kerman University of Medical Sciences, Kerman, Iran.
Bulvd. 22 Bahman, Kerman, Iran.
Tel.: +98 91 3247 4293
Email: soheilaminizadeh@gmail.com
Handling editor:
Michal Heger
Department of Pharmaceutics, Utrecht University, the Netherlands
Department of Chemistry, Utrecht University, Utrecht, the Netherlands
Department of Pathology, Erasmus Medical Center, the Netherlands
Department of Pharmaceutics, Jiaxing University Medical College, Zhejiang, China

